QFM064: Irresponsible AI Reading List April 2025
Everything that I found interesting last month about the irresponsible use of AI.
Tags: qfm, irresponsible, ai, reading, list, april, 2025
 Source: Photo by Luis Villasmil on Unsplash
Source: Photo by Luis Villasmil on Unsplash
This month’s Irresponsible AI Reading List reveals fundamental gaps between AI hype and practical reality. Recent AI Model Progress Feels Mostly Like Bullshit provides a direct assessment of recent AI advancements, arguing that despite marketing claims and test improvements, these models fail to deliver significant practical benefits or economic value in real-world applications. This connects to There is no Vibe Engineering, which challenges the concept of “vibe coding” popularised by Andrej Karpathy, arguing that whilst AI assists with prototyping, it lacks the robustness required for true software engineering that involves designing evolutive systems.
Security vulnerabilities expose systemic weaknesses across multiple fronts. Novel Universal Bypass for All Major LLMs demonstrates a new prompt injection technique that bypasses safety guardrails in major AI models from OpenAI, Google, and Microsoft, highlighting insufficient reliance on Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback for model alignment. Meanwhile, AI-generated code could be a disaster for the software supply chain reveals how AI generates ‘hallucinated’ package dependencies that create opportunities for supply-chain attacks through phantom libraries, particularly affecting JavaScript ecosystems.
Surveillance and geopolitical threats demonstrate AI’s role in authoritarian applications. The Shocking Far-Right Agenda Behind the Facial Recognition Tech Used by ICE and the FBI exposes how Clearview AI’s facial recognition technology, built from scraped online images, enables warrantless surveillance targeting immigrants and political adversaries.
This connects to The one interview question that will protect you from North Korean fake workers, which reveals how North Korean agents use generative AI to create fake LinkedIn profiles for remote employment infiltration.
Content manipulation and attribution challenges highlight AI’s impact on information integrity. LLMs Don’t Reward Originality, They Flatten It examines how large language models favour consensus over original ideas, creating ‘LLM flattening’ that dilutes unique insights in favour of widely recognised concepts. Technical evidence of manipulation appears in New ChatGPT Models Seem to Leave Watermarks on Text, which identifies special Unicode character watermarks in ChatGPT output, though OpenAI clarifies these as unintentional quirks from reinforcement learning rather than deliberate watermarks.
Human deception and verification receive attention through practical scenarios. What it’s like to interview a software engineer preparing with AI describes candidates using AI for interview preparation, revealing gaps in truthfulness that require deeper situational questioning to assess genuine abilities. Creative countermeasures appear in Benn Jordan’s AI poison pill and the weird world of adversarial noise, which demonstrates embedding imperceptible adversarial noise into audio files to prevent unauthorised AI training on music, though current methods demand significant computational resources.
As always, the Quantum Fax Machine Propellor Hat Key will guide your browsing. Enjoy!

 There is no Vibe Engineering: Sergey Tselovalnikov discusses the concept of “vibe coding,” a term popularized by Andrej Karpathy, where coding is done by interacting with AI agents to produce code instead of manually writing it. Despite the buzz, vibe coding is seen as lacking the robustness needed for true software engineering, which involves designing systems that can evolve and handle real-world demands. The article argues that while AI can aid in prototype development, it does not replace the comprehensive role of software engineering, which integrates programming and systems design over the lifecycle of a software product.
There is no Vibe Engineering: Sergey Tselovalnikov discusses the concept of “vibe coding,” a term popularized by Andrej Karpathy, where coding is done by interacting with AI agents to produce code instead of manually writing it. Despite the buzz, vibe coding is seen as lacking the robustness needed for true software engineering, which involves designing systems that can evolve and handle real-world demands. The article argues that while AI can aid in prototype development, it does not replace the comprehensive role of software engineering, which integrates programming and systems design over the lifecycle of a software product.
#VibeCoding #AI #SoftwareEngineering #Prototyping #Technology
 Recent AI Model Progress Feels Mostly Like Bullshit: The article explores the author’s experiences and observations of recent advancements in AI models, particularly in the context of software security. Despite the hype and claimed improvements in AI capabilities, the author argues that these advancements do not translate into significant practical benefits or economic usefulness, based on their internal benchmarks and experiences. The text suggests that AI models may be becoming better at test-specific tasks but still fail to generalize effectively or outperform regular engineering efforts in real-world scenarios.
Recent AI Model Progress Feels Mostly Like Bullshit: The article explores the author’s experiences and observations of recent advancements in AI models, particularly in the context of software security. Despite the hype and claimed improvements in AI capabilities, the author argues that these advancements do not translate into significant practical benefits or economic usefulness, based on their internal benchmarks and experiences. The text suggests that AI models may be becoming better at test-specific tasks but still fail to generalize effectively or outperform regular engineering efforts in real-world scenarios.
#AI #technology #machinelearning #progress #innovation
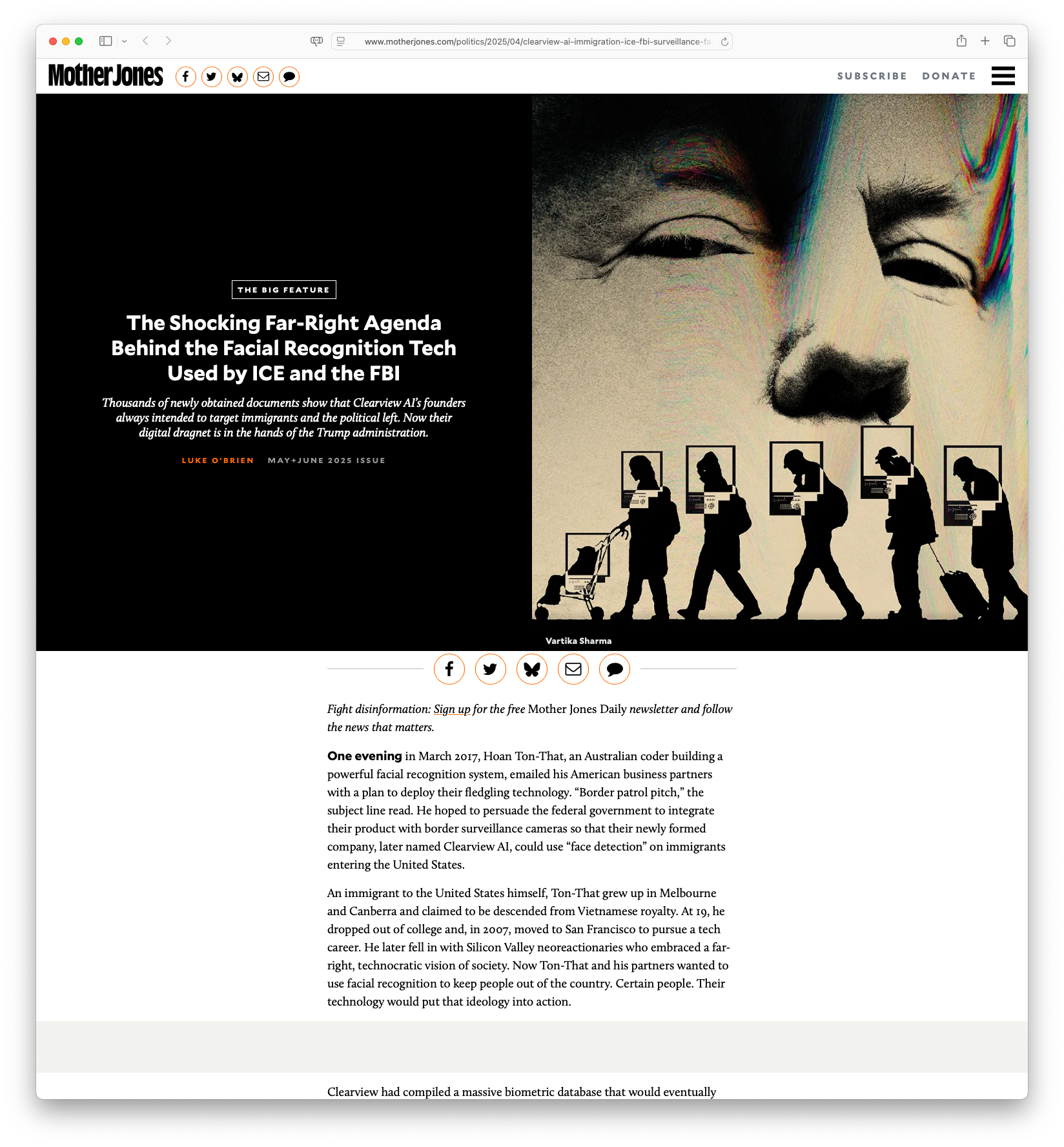
 The Shocking Far-Right Agenda Behind the Facial Recognition Tech Used by ICE and the FBI: Clearview AI, a controversial facial recognition company founded by Hoan Ton-That, has been disclosed to have deep ties with far-right agendas and intentions to target immigrants and political adversaries through its technology. The company amassed a vast database from images scraped online, providing authorities with powerful surveillance tools without warrants. Funded by influential right-wing figures, their technology has been integrated into various law enforcement agencies, including ICE, reflecting a move towards increased state surveillance and potential misuse against marginalized communities.
The Shocking Far-Right Agenda Behind the Facial Recognition Tech Used by ICE and the FBI: Clearview AI, a controversial facial recognition company founded by Hoan Ton-That, has been disclosed to have deep ties with far-right agendas and intentions to target immigrants and political adversaries through its technology. The company amassed a vast database from images scraped online, providing authorities with powerful surveillance tools without warrants. Funded by influential right-wing figures, their technology has been integrated into various law enforcement agencies, including ICE, reflecting a move towards increased state surveillance and potential misuse against marginalized communities.
#FacialRecognition #Privacy #ClearviewAI #Surveillance #FarRight
 What it’s like to interview a software engineer preparing with AI: This article discusses a unique experience during a software engineering interview, where the candidate admitted to using AI for preparation. Initially impressive, the candidate’s inability to answer certain technical questions revealed gaps in their truthfulness. The article emphasizes the importance of deeper situational questions in interviews to discern the genuine abilities of applicants in the age of AI.
What it’s like to interview a software engineer preparing with AI: This article discusses a unique experience during a software engineering interview, where the candidate admitted to using AI for preparation. Initially impressive, the candidate’s inability to answer certain technical questions revealed gaps in their truthfulness. The article emphasizes the importance of deeper situational questions in interviews to discern the genuine abilities of applicants in the age of AI.
#AI #JobInterviews #SoftwareEngineering #TechHiring #Integrity
 The one interview question that will protect you from North Korean fake workers: The FBI and CrowdStrike’s Adam Meyers discuss the threat of North Korean agents infiltrating companies under the guise of employees. These agents use generative AI to create fake LinkedIn profiles to secure jobs, often working remotely through laptop farms. A unique interview question, “How fat is Kim Jong Un?”, is used to filter out these infiltrators as it causes them to drop out of the recruitment process immediately.
The one interview question that will protect you from North Korean fake workers: The FBI and CrowdStrike’s Adam Meyers discuss the threat of North Korean agents infiltrating companies under the guise of employees. These agents use generative AI to create fake LinkedIn profiles to secure jobs, often working remotely through laptop farms. A unique interview question, “How fat is Kim Jong Un?”, is used to filter out these infiltrators as it causes them to drop out of the recruitment process immediately.
#CyberSecurity #NorthKorea #AI #JobInterview #FBI
 Benn Jordan’s AI poison pill and the weird world of adversarial noise: Benn Jordan demonstrates how to embed imperceptible adversarial noise—an “AI poison pill”—into audio files to prevent generative AI from training on music, highlighting a proof‑of‑concept that works in real-world settings and can be updated in response to AI counter‑moves . He argues that while this method reveals how datasets and models interact and may deter unauthorised training, its current form demands significant compute power, limiting it to early-stage defence strategies.
Benn Jordan’s AI poison pill and the weird world of adversarial noise: Benn Jordan demonstrates how to embed imperceptible adversarial noise—an “AI poison pill”—into audio files to prevent generative AI from training on music, highlighting a proof‑of‑concept that works in real-world settings and can be updated in response to AI counter‑moves . He argues that while this method reveals how datasets and models interact and may deter unauthorised training, its current form demands significant compute power, limiting it to early-stage defence strategies.
#DevTools #MusicTech #AI #AdversarialNoise #CopyrightDefense
 LLMs Don’t Reward Originality, They Flatten It: The article discusses how large language models (LLMs) tend to reward consensus rather than originality, posing challenges for unique ideas to gain visibility. This phenomenon, referred to as ‘LLM flattening,’ results in the dilution of nuanced, original insights in favor of widely recognized concepts. To counteract this, the article suggests strategies such as clearly labeling ideas, incorporating branding, and extensive distribution to improve the chances of new concepts being recognized in AI-generated responses. It emphasizes the need for playing the long game as originality can eventually impact discussions, even without direct attributions.
LLMs Don’t Reward Originality, They Flatten It: The article discusses how large language models (LLMs) tend to reward consensus rather than originality, posing challenges for unique ideas to gain visibility. This phenomenon, referred to as ‘LLM flattening,’ results in the dilution of nuanced, original insights in favor of widely recognized concepts. To counteract this, the article suggests strategies such as clearly labeling ideas, incorporating branding, and extensive distribution to improve the chances of new concepts being recognized in AI-generated responses. It emphasizes the need for playing the long game as originality can eventually impact discussions, even without direct attributions.
#Originality #AI #Innovation #LanguageModels #SEO
 Novel Universal Bypass for All Major LLMs: Researchers at HiddenLayer have developed a new, universal prompt injection technique that can bypass instruction hierarchies and safety guardrails in major AI models such as those from OpenAI, Google, Microsoft, and others. This method, using Policy Puppetry Prompt Injection, exploits systemic weaknesses in how AI models are trained, allowing harmful content generation from these systems. The technique shows that reliance on Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) for model alignment is insufficient, highlighting the need for proactive security testing and real-time monitoring solutions like HiddenLayer’s AISec Platform. This poses significant implications for AI safety and risk management in sensitive environments.
Novel Universal Bypass for All Major LLMs: Researchers at HiddenLayer have developed a new, universal prompt injection technique that can bypass instruction hierarchies and safety guardrails in major AI models such as those from OpenAI, Google, Microsoft, and others. This method, using Policy Puppetry Prompt Injection, exploits systemic weaknesses in how AI models are trained, allowing harmful content generation from these systems. The technique shows that reliance on Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) for model alignment is insufficient, highlighting the need for proactive security testing and real-time monitoring solutions like HiddenLayer’s AISec Platform. This poses significant implications for AI safety and risk management in sensitive environments.
#AI #Security #MachineLearning #AIModels #TechNews

 New ChatGPT Models Seem to Leave Watermarks on Text: Recent developments suggest that the newer ChatGPT-o3 and GPT-o4 mini models embed special character watermarks in the generated text. These watermarks are primarily special Unicode characters that resemble regular spaces, detectable via text editors or specific online tools. While initially problematic, recent updates imply that the issue may have been resolved, and OpenAI has clarified that these were not intentional watermarks but rather quirks from large-scale reinforcement learning.
New ChatGPT Models Seem to Leave Watermarks on Text: Recent developments suggest that the newer ChatGPT-o3 and GPT-o4 mini models embed special character watermarks in the generated text. These watermarks are primarily special Unicode characters that resemble regular spaces, detectable via text editors or specific online tools. While initially problematic, recent updates imply that the issue may have been resolved, and OpenAI has clarified that these were not intentional watermarks but rather quirks from large-scale reinforcement learning.
#ChatGPT #AI #Watermarking #OpenAI #Technology
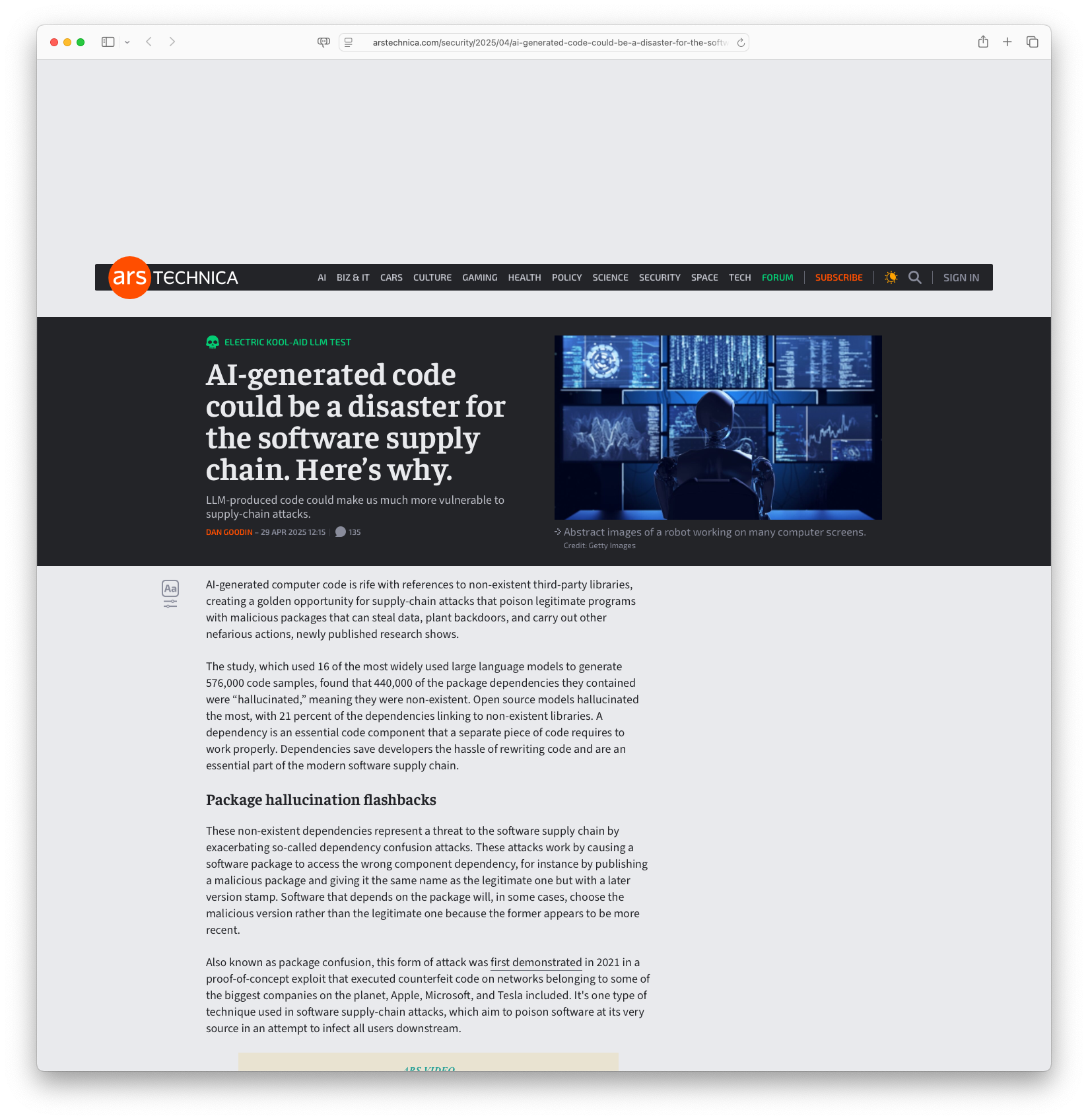
 AI-generated code could be a disaster for the software supply chain. Here’s why.: AI-generated code poses a new cyber threat by creating ‘hallucinated’ package dependencies. Research shows this issue could open doors to supply-chain attacks where malicious code is introduced using non-existent third-party libraries. Such attacks rely on AI’s suggestion of phantom packages, making unsuspecting developers vulnerable to compromised systems. Despite the complex network of dependencies within AI-generated code, this bug persists across multiple queries, making it an exploitable weakness. Open-source models are particularly prone to these hallucinations, with JavaScript packages exhibiting higher rates than Python due to its expansive ecosystem. As AI continues to grow in generating code, it becomes crucial for developers to detect and mitigate these vulnerabilities to protect against potential cybersecurity threats.
AI-generated code could be a disaster for the software supply chain. Here’s why.: AI-generated code poses a new cyber threat by creating ‘hallucinated’ package dependencies. Research shows this issue could open doors to supply-chain attacks where malicious code is introduced using non-existent third-party libraries. Such attacks rely on AI’s suggestion of phantom packages, making unsuspecting developers vulnerable to compromised systems. Despite the complex network of dependencies within AI-generated code, this bug persists across multiple queries, making it an exploitable weakness. Open-source models are particularly prone to these hallucinations, with JavaScript packages exhibiting higher rates than Python due to its expansive ecosystem. As AI continues to grow in generating code, it becomes crucial for developers to detect and mitigate these vulnerabilities to protect against potential cybersecurity threats.
#AI #CyberSecurity #SupplyChain #OpenSource #MachineLearning
Regards,
M@
[ED: If you’d like to sign up for this content as an email, click here to join the mailing list.]
Originally published on quantumfaxmachine.com and cross-posted on Medium.
hello@matthewsinclair.com | matthewsinclair.com | bsky.app/@matthewsinclair.com | masto.ai/@matthewsinclair | medium.com/@matthewsinclair | xitter/@matthewsinclair |

